Oxygen FAQ
Up to date, expert answers to frequently asked questions (FAQ) about oxygen supply systems, respiratory care and pulse oximetry written by OCC & collaborators.
Pulse Oximetry
What is the average root mean square error (ARMS)?
The Average Root Mean Square error or root mean square deviation (known as ARMS) is a commonly used metric for pulse oximeter oxygen saturation (SpO2) performance and is used by regulatory agencies to determine how well a pulse oximeter performs. Sometimes referred to as “Accuracy Root Mean Square error,” ARMS is the square root of the mean of the squared deviations between the pulse oximeter SpO2 measurement and the gold-standard functional oxygen saturation (SaO2) measurement obtained from an arterial blood sample analyzed on a co-oximeter. ARMS approximates the mean absolute deviation (MAD) between SpO2 and SaO2. It is always a positive value, so it cannot indicate whether SpO2 is negatively or positively biased for SaO2. Higher ARMS implies worse performance. ARMS is best referred to as a measure of performance (rather than accuracy).
𝐴𝑅𝑀𝑆= √(𝑏𝑖𝑎𝑠^2+𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛^2)
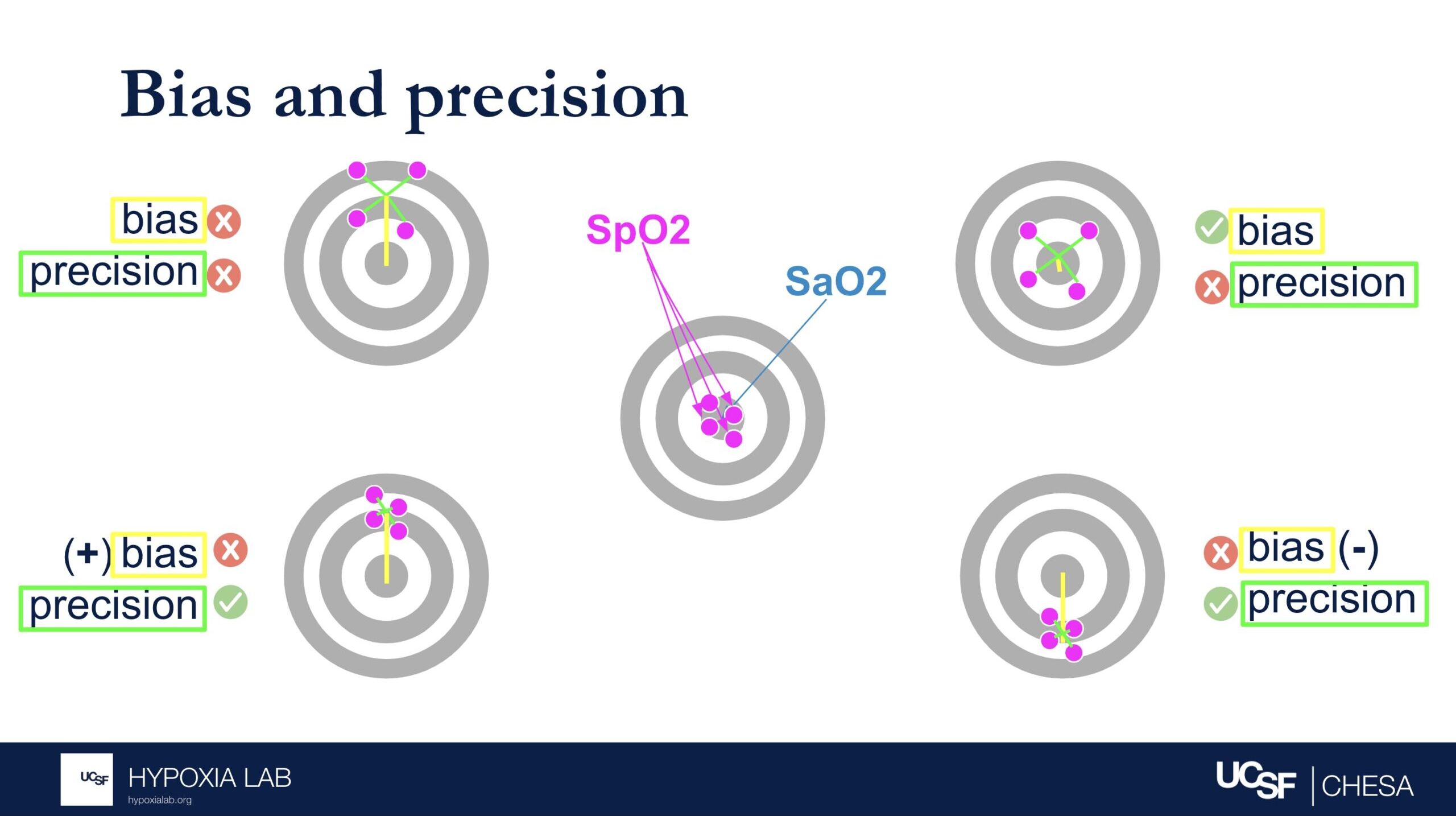
Bias describes whether the SpO2 over- or underestimates the true SaO2 (i.e. magnitude and direction of error relative to the bullseye of the target). Precision describes how much random error there is (i.e. magnitude but not direction relative to the bulleye of the target). See figure 1 below.
If either or both components of ARMS (bias or precision) is very large, then ARMS will be greater than the acceptable limit and will not be considered an acceptably performing pulse oximeter. Conversely, a device can have no error in one of the components but still have error in the other component.
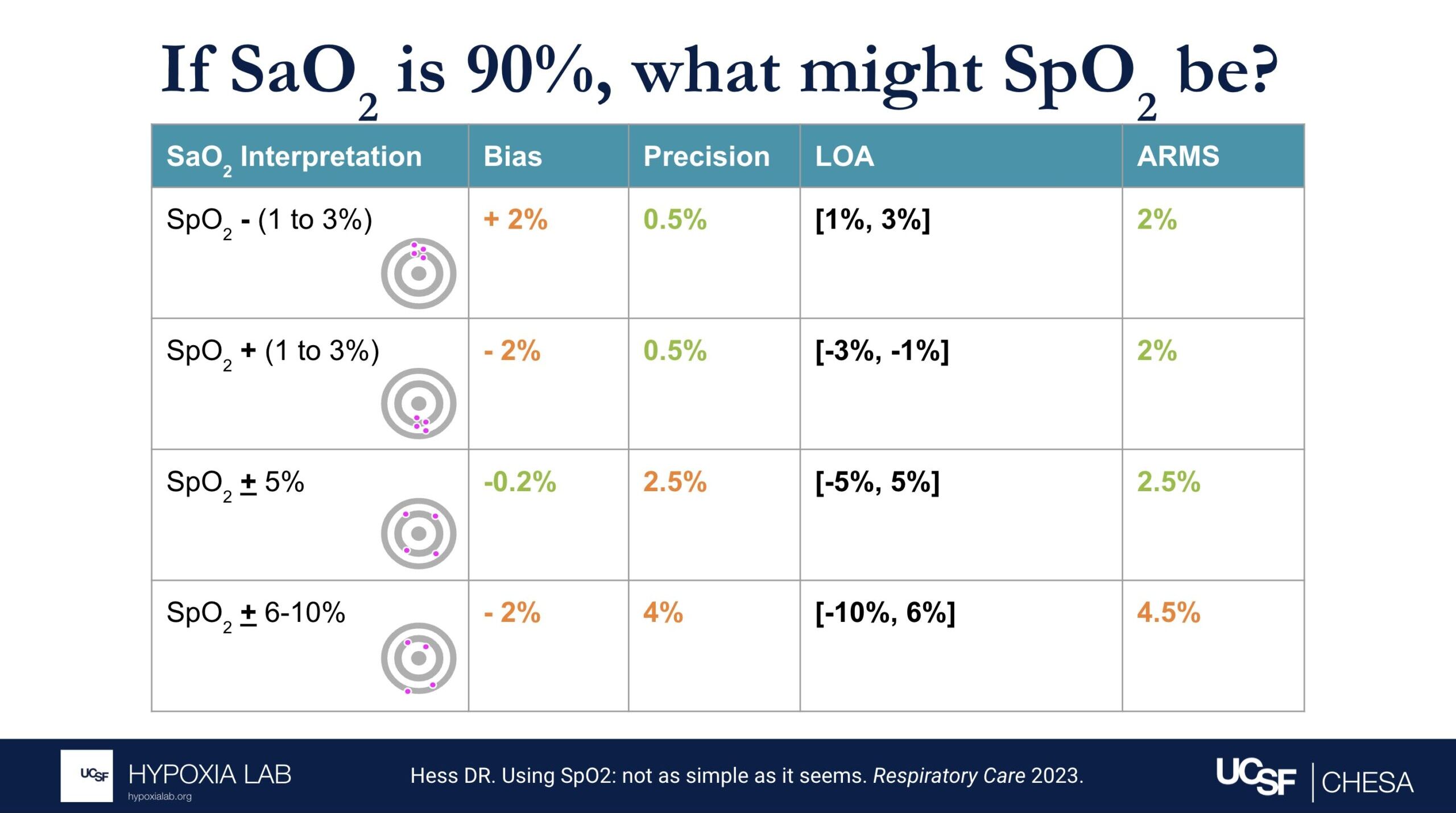
Several examples in the table and figures below help illustrate the challenges in interpreting ARMS and applying this metric at the clinical bedside. For example, if there is no bias and only imprecision (i.e. random error), then an ARMS of 3% implies that most of the time a pulse oximeter SpO2 of 90% is within + 3% (87%-93%) of the true oxygen saturation (SaO2, as measured by a blood gas co-oximeter). However, if bias (e.g. positive bias in patients with darker skin pigment) is also present, then interpreting the ARMS is more difficult.
The 2013 guidance from the FDA recommends an acceptable limit of ARMS ≤3% for transmittance devices and ARMS ≤3.5% for reflectance devices or ear clip devices. The latest 2025 Draft Guidance from the FDA recommends ARMS <3% for all devices, with the addition of a 95% confidence interval. It is important to recognize that even a small difference in ARMS between devices, especially if concurrent random error and bias exist, can reflect a large difference in their performance. See Figure 2 below from Sjoding et al 2022.
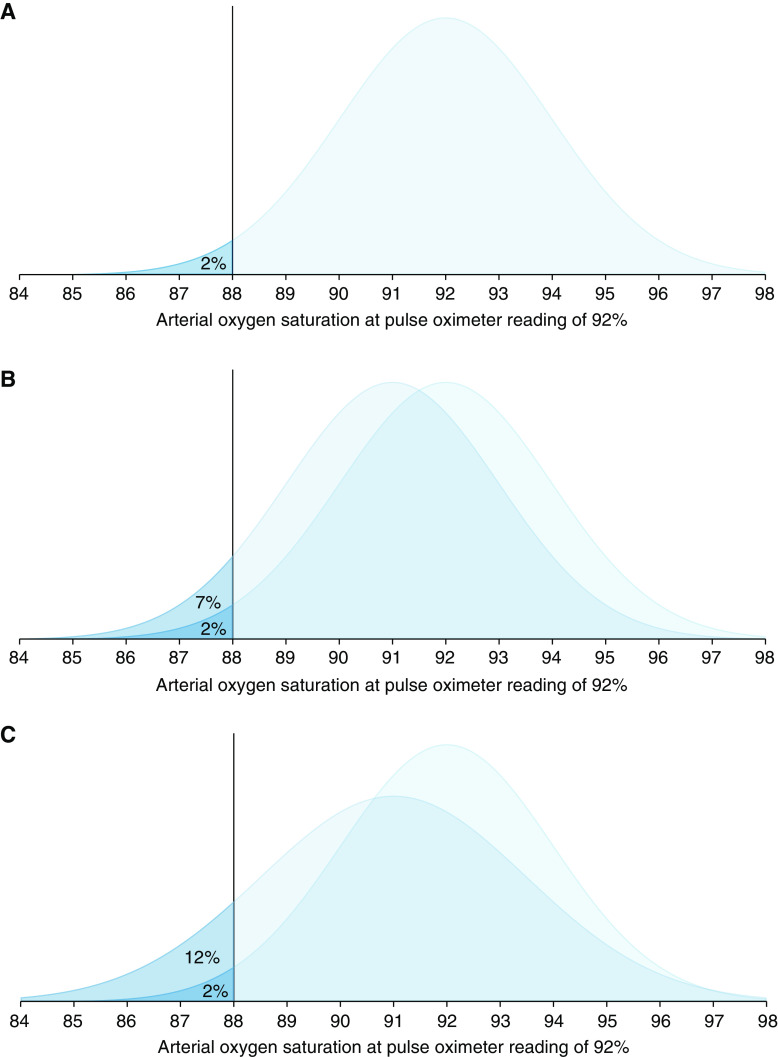
The figure above is reproduced from Sjoding et al 2022: “Distribution of arterial oxygen saturation and saturation rate <88% when the pulse oximeter is reading at 92%. (A) Pulse oximeter with 2% random error. (B) Overlaid distribution of a pulse oximeter with 2% random error and 1% bias. (C) Overlaid distribution of a pulse oximeter with 2.5% random error and 1% bias.”
Sjoding et al, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2022; This figure is open access and distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives License 4.0 Copyright © 2023 by the American Thoracic Society
References:
Clinical Application of ARMS in Pulse Oximetry – Clinimark June 2021;
Keywords: bias, standard deviation, Arms, ARMS